1. NBR (Nitrile Butadiene Rubber): The Industrial All-Rounder
As a star in synthetic rubber, NBR is produced via copolymerization of butadiene and acrylonitrile, valued for its exceptional physical and chemical properties in industrial and civil applications. In automotive manufacturing, it forms seals and oil seals for critical components; in industrial hoses and cables, it withstands pressure and transmits energy; in rubber rollers and printing rollers, it ensures precise printing. It also appears in daily items like shoe soles, gloves, adhesive tapes, hoses, seals, and gaskets.
Physical Properties Overview:
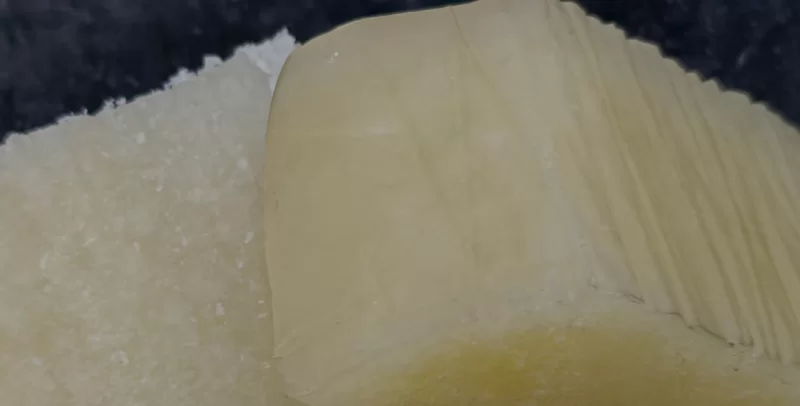

2. NR (Natural Rubber): Nature’s Elastic Treasure
Derived from natural sources, NR’s Crystallization characteristics endows it with high strength, superior elasticity, and ductility. As a core material for tires, seals, and shock-absorbing components, it ensures transportation safety. In daily life, it enhances the comfort and durability of rubber gloves, sports balls, mats, protective gear, and shoe soles. In healthcare, it supports flexible manufacturing of IV tubes, breathing masks, artificial organs, and hemostatic bandages.
Physical Properties Overview:
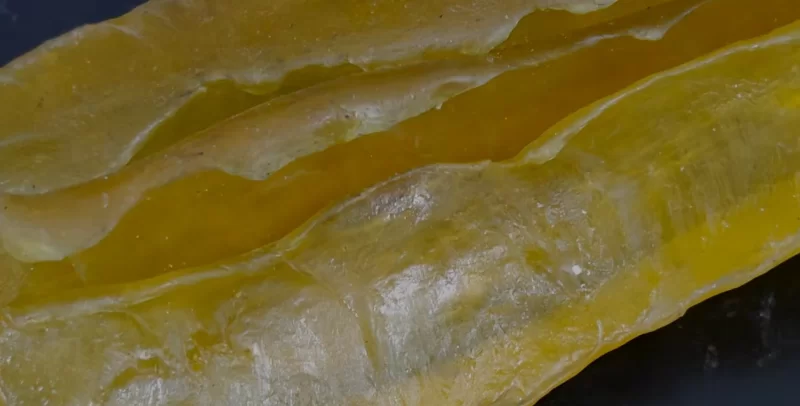

3. CR (Chloroprene Rubber): All-Round High-Performance Synthetic Rubber
Formed by polymerizing 2-chloro-1,3-butadiene, CR boasts outstanding physical-mechanical properties: high tensile strength, significant elongation, and reversible crystallinity, paired with excellent adhesion, aging resistance, heat/oil/chemical corrosion resistance, and weather/ozone resistance (second only to EPDM and butyl rubber). It excels in tires, heat-resistant conveyor belts, oil/chemical-resistant hoses, automotive parts, cable insulation, and building waterproofing sheets.
Physical Properties Overview:
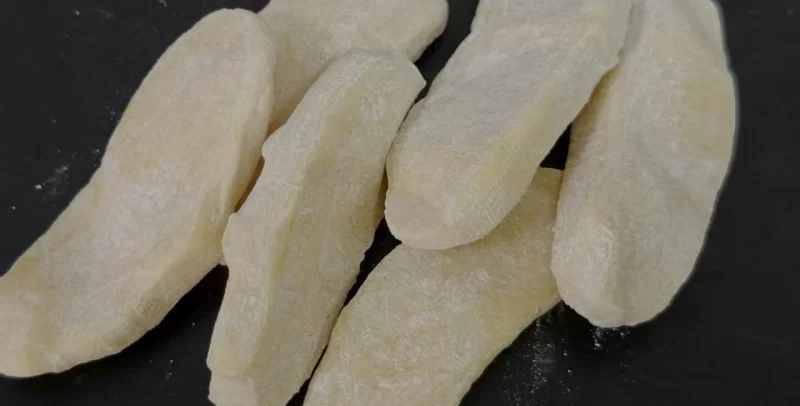

4. EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer): The Chemically Stable Electrical Insulator
Copolymerized from ethylene, propylene, and a small amount of non-conjugated diene, EPDM features exceptional chemical stability (resistant to oxygen, ozone, heat, aqueous solutions, and polar solvents) and superior electrical insulation (resistant to corona discharge). It is critical for electrical insulation materials like cable sheaths and electronic component seals, widely used in automotive, construction, electronics, and aerospace industries.
Physical Properties Overview:

5. SBR (Styrene Butadiene Rubber): The Intelligent Upgrade Of Natural Rubber
Synthesized via styrene-butadiene copolymerization, SBR mimics natural rubber in physical and processing properties but surpasses it in wear, heat, and aging resistance, as well as vulcanization speed. It enhances durability in traditional rubber products like tires and shoe soles.
Physical Properties Overview:

6. ACM (Acrylate Rubber): Guardian Of High-Temperature, Oil-Intensive Environments
Polymerized from acrylate monomers, ACM’s saturated main chain and polar ester side groups grant it "superpowers" of high-temperature, oil, and aging resistance. It thrives in harsh environments of automotive, chemical, and petroleum industries—high temperature/pressure, strong chemical corrosion—serving as indispensable protection for critical components.
Physical Properties Overview:

7. MVQ (Methyl Vinyl Silicone Rubber): The Extreme-Temperature Resistant Long-Life Rubber
With a silicon-based main chain and methyl/vinyl side chains, MVQ features a saturated structure for superior aging and chemical resistance. It operates seamlessly in extreme temperatures (-120 to 280℃), making it the top choice for aerospace, electronics, and other cutting-edge fields demanding ultimate reliability.
Physical Properties Overview:

8. FKM (Fluororubber): The Industrial Fireproof Champion
Copolymerized from fluorohydrocarbon and hydrogenated hydrocarbon, FKM is a high-performance fluoroelastomer renowned for resistance to high temperature, oil, chemicals, and ozone. It excels in aerospace, automotive, and chemical industries, serving as the ultimate protection in high-temperature/pressure and strongly corrosive environments.
Physical Properties Overview:

9. HNBR (Hydrogenated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber): The High-Performance Elastomer Masterpiece
Derived from NBR via hydrogenation, HNBR features saturated carbon-carbon double bonds, combining oil, heat, oxidation, chemical, and cold resistance with high strength and wear resistance. It supports advanced equipment in petrochemical, automotive, and other frontline industries.
Physical Properties Overview:


 Select Language
Select Language